Dieter Hörsch, MD: For Patients With Bronchopulmonary Neuroendocrine Tumors, Lanreotide Autogel May Be Beneficial
ESMO Congress 2021
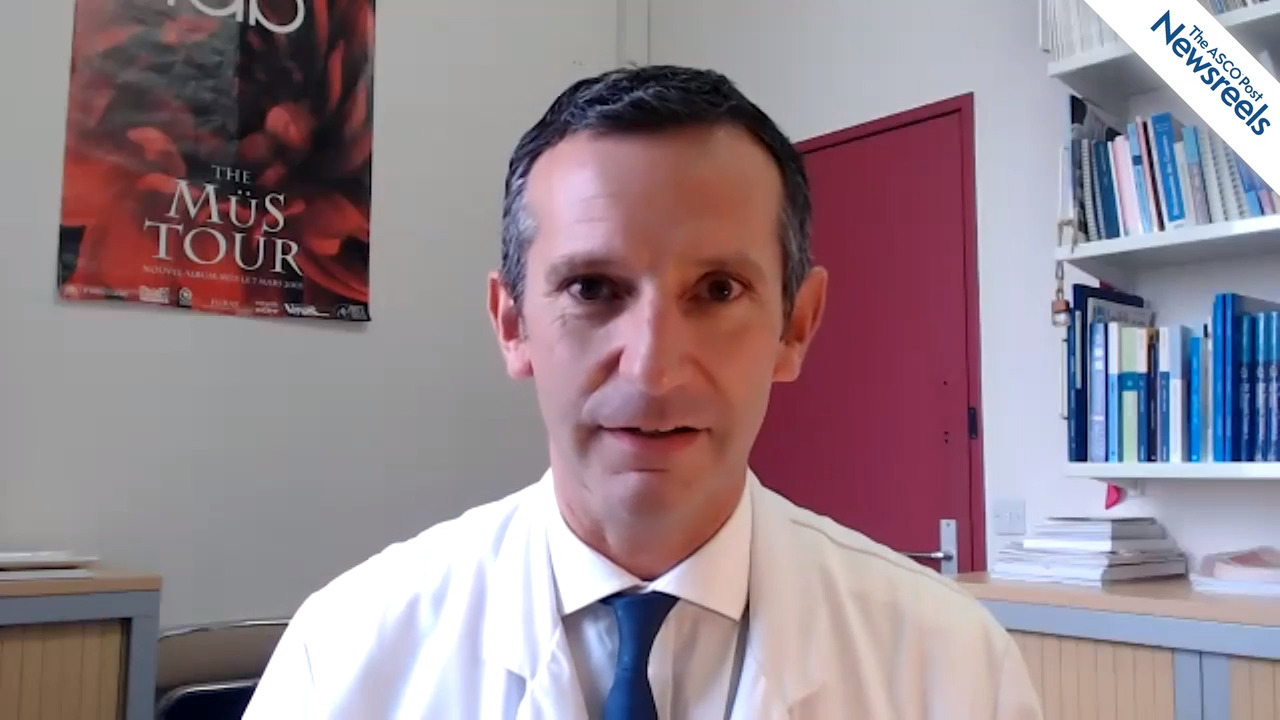
Dieter Hörsch, MD, of Germany’s Central Clinic in Bad Berka, discusses phase III results from the SPINET trial, the largest prospective study to date of the somatostatin analog lanreotide autogel. The study suggests that this agent may prove to be an appropriate treatment option for patients with somatostatin receptor–positive bronchopulmonary neuroendocrine tumors, especially typical carcinoids (Abstract 1096O).
The ASCO Post Staff
Benjamin Besse, MD, PhD, of the Institut Gustave Roussy, discusses final phase III findings from the Atalante-1 trial, which explored the question of whether the OSE2101 vaccine is more beneficial than standard treatment for patients with HLA-A2–positive non–small cell lung cancer after immune checkpoint inhibitors are no longer effective (Abstract LBA47).
The ASCO Post Staff
Susana N. Banerjee, MBBS, PhD, of The Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust, discusses phase II results of the EORTC-1508 trial, the first study to combine an anti–PD-L1 antibody, atezolizumab, with bevacizumab and the COX1/2 inhibitor acetylsalicylic acid as treatment for patients with ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal adenocarcinoma (Abstract LBA32).
The ASCO Post Staff
Gabriel N. Hortobagyi, MD, of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, discusses results from the MONALEESA-2 trial, which showed that adding the CDK4/6 inhibitor ribociclib to first-line hormonal therapy prolongs survival by 1 year for postmenopausal women with hormone receptor–positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer. As a result, he believes it should be considered the preferred treatment option (Abstract LBA17).
The ASCO Post Staff
Javier Cortés, MD, PhD, of Barcelona’s IOB Institute of Oncology, discusses phase III data from the DESTINY-Breast03 study, which support trastuzumab deruxtecan becoming the standard of care for second-line treatment of women with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer (Abstract LBA1).
The ASCO Post Staff
Susana N. Banerjee, MBBS, PhD, of The Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust, discusses phase I results that have generated interest in the combination of the RAF/MEK inhibitor VS-6766 and the FAK inhibitor defactinib for patients with recurrent low-grade serous ovarian cancer, a disease that typically has limited response to conventional chemotherapy and hormonal therapy. The data support ongoing investigation (Abstract 725MO).