Naveen S. Vasudev, PhD, MBChB, on RCC: Changing the Dosing Schedule of Ipilimumab Plus Nivolumab
ESMO Congress 2021
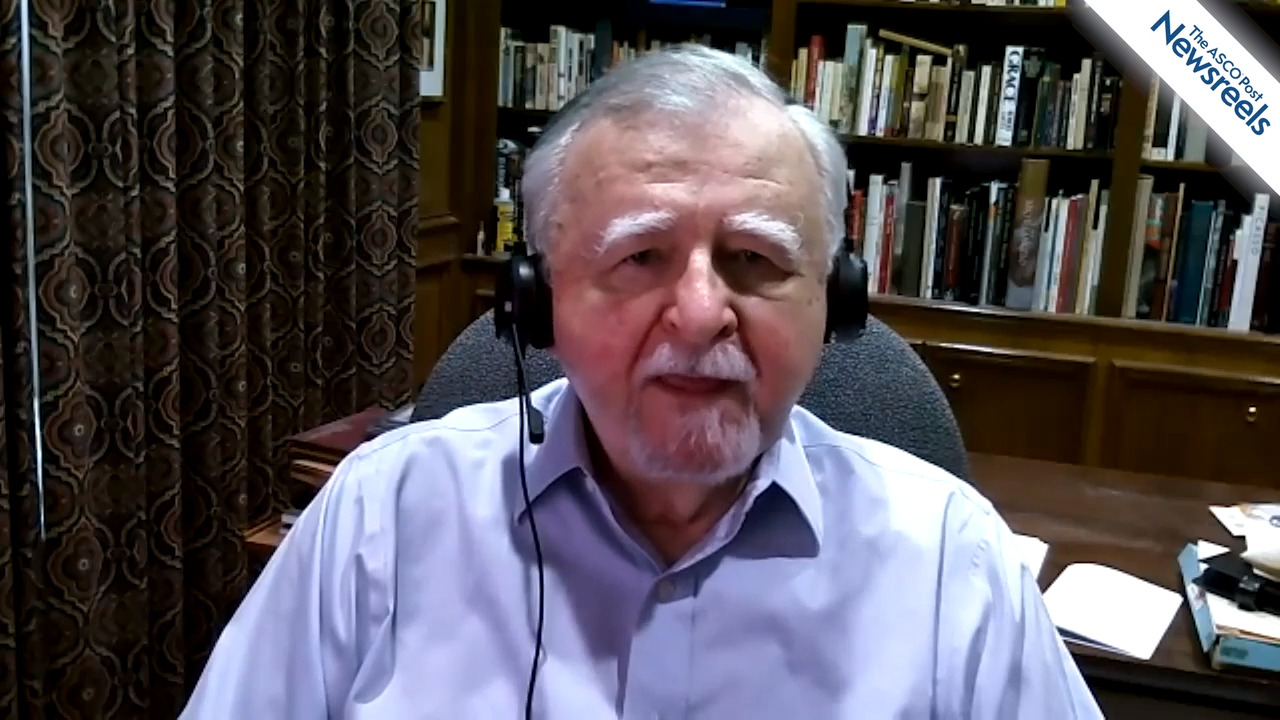
Naveen S. Vasudev, PhD, MBChB, of the University of Leeds, discusses phase II results from the PRISM trial, which showed that giving ipilimumab every 12 weeks instead of every 3 weeks, in combination with nivolumab, led to lower rates of grade 3 and 4 toxicities in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. Efficacy appeared to be comparable between both arms (Abstract LBA29).
The ASCO Post Staff
Gabriel N. Hortobagyi, MD, of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, discusses results from the MONALEESA-2 trial, which showed that adding the CDK4/6 inhibitor ribociclib to first-line hormonal therapy prolongs survival by 1 year for postmenopausal women with hormone receptor–positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer. As a result, he believes it should be considered the preferred treatment option (Abstract LBA17).
The ASCO Post Staff
Nicoletta Colombo, MD, of the Istituto Europeo Oncologico, discusses phase III results that showed improvements in progression-free and overall survival with a combination of pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy, compared with placebo and chemotherapy, for patients with persistent, recurrent, or metastatic cervical cancer. These benefits were seen regardless of PD-L1 expression and concomitant bevacizumab use, suggesting that pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy, with or without bevacizumab, may be a new standard of care for this population (Abstract LBA2).
The ASCO Post Staff
Javier Cortés, MD, PhD, of Barcelona’s IOB Institute of Oncology, discusses phase III data from the DESTINY-Breast03 study, which support trastuzumab deruxtecan becoming the standard of care for second-line treatment of women with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer (Abstract LBA1).
The ASCO Post Staff
Jenny F. Seligmann, MBChB, PhD, of the University of Leeds, discusses phase II findings that suggest adavosertib improved progression-free survival, compared with active monitoring, by inhibiting the WEE1 kinase in patients with RAS- and TP53-mutant metastatic colorectal cancer. In the trial, adavosertib’s activity tended to be even greater in left-sided tumors (Abstract 382O).
The ASCO Post Staff
Filippo Pietrantonio, MD, and Federica Morano, MD, both of the Istituto Nazionale dei Tumori, discuss results from the MAYA trial, which provided proof of concept that temozolomide-induced hypermutation may be exploited to achieve durable responses to low-dose ipilimumab plus nivolumab in patients with microsatellite stable metastatic colorectal cancer (Abstract 383O).