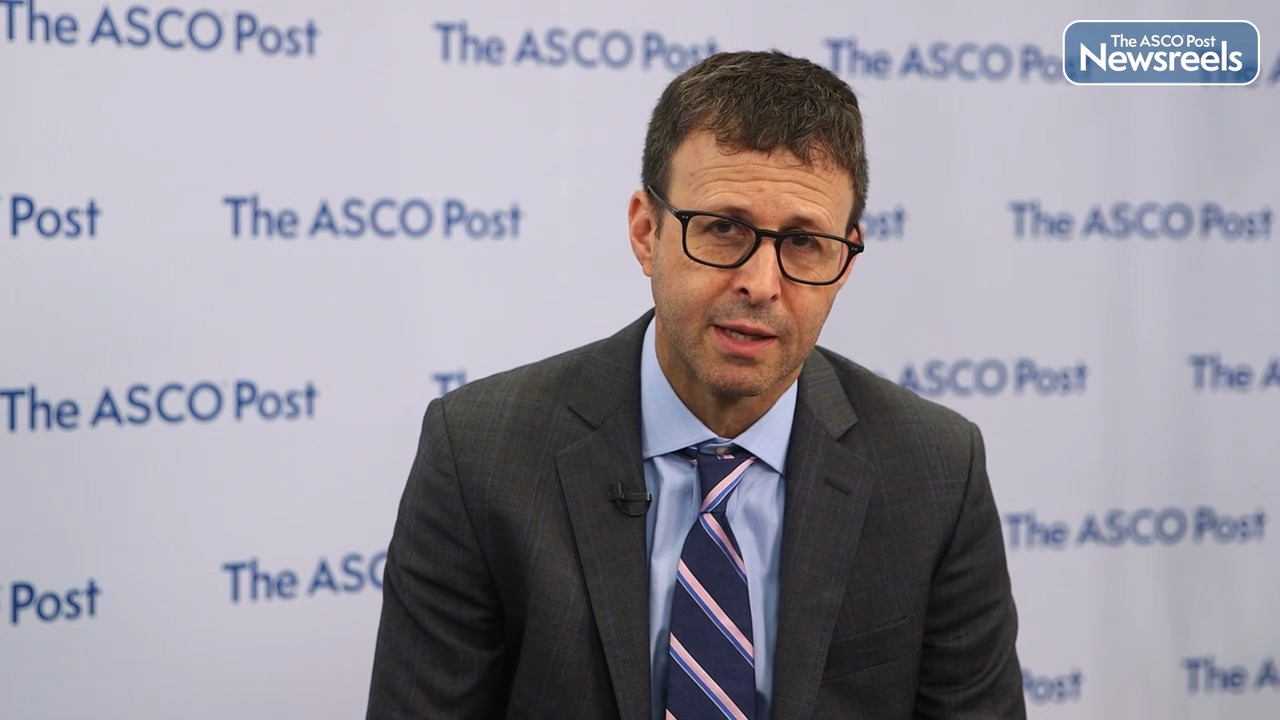
Nancy Davidson, MD: In It for the Long Haul: Outcomes in Hormone Receptor–Positive Breast Cancer
2022 ASCO Annual Meeting
Nancy Davidson, MD, of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, reviews results from four abstracts about the importance of long-term follow-up in studies of adjuvant endocrine therapy for hormone receptor–positive breast cancer. Because the natural history of hormone receptor–positive breast cancer is long, an effort is underway to improve selection of patients by clinical parameters or biomarkers, refine the endocrine therapy background, and administer more effective combinations of endocrine therapy with other agents.
Transcript
Disclaimer: This video transcript has not been proofread or edited and may contain errors.
Nancy Davidson:
One of the vexing problems in the management of hormone receptor positive breast cancer is that patients still relapse. We know a lot about the natural history of the disease, and we know that sometimes the relapses can be later. So, we had the opportunity recently to hear the results of four clinical trials that try to look at longer term outcomes in hormone receptor positive breast cancer. These trials in my estimation, try to tackle a couple of different ways that we could improve on this situation. In some cases, they try to refine the selection of patients either by clinical parameters or by molecular tests. In other cases, they try to look at combinations of endocrine therapy or sequences of endocrine therapy. In some cases, they also take a look at the addition of other agents to endocrine therapy. And then finally, we sometimes look at the duration of endocrine therapy.
Now, the first trial that I want to talk about in this context is that a retrospective analysis of the trials from the IBCSG looking at the big trial, the soft trial, and the text trial. This reanalysis was done of this trial, these trials, to try to look at the subsets of high risk patients within those trials, those who had node positive disease or node greater than four nodes, or one to three positive nodes with high risk features. And that's because we wanted to look at them in the context of some of the CDK4/6 inhibitors trials that have also emerged. What came out is that there is an advantage of the endocrine therapy in these trials over the long haul. It also provides us with a baseline, so that we can use this in the future for trial designs for addition of new agents. Wonderful to see that long term follow up.
A second trial looked at older patients. Now this is a really unmet need in early stage breast cancer. This trial focus specifically on patients 70 or over, and it looked at a genomic index as a way of trying to select for or against the use of chemotherapy in addition to endocrine therapy. This genomic index hasn't really been used elsewhere and this trial did show at the end of the day that this index did not help to select for or against the use of chemotherapy. The patients that had high genomic index didn't do better with the chemotherapy. So, as a consequence, we won't be using it further but congratulations to them, we're focusing on high risk elderly patients. Another trial looked at ovarian function suppression in the context of tamoxifen. Long follow up again, it supports the use of ovarian function suppression as we've done in the past, but only two years actually. So, an effort to try to deescalate the ovarian function suppression, wonderful to see that long term follow up.
And then finally the last trial looked at whether or not we should use Denosumab, a bone strengthening agent in addition to hormone therapy in postmenopausal receptor positive breast cancer. We already know that this can help to decrease fractures and what the long term follow up of this trial has shown and exploratory endpoints that Denosumab also decreases the risk of recurrence of breast cancer and appears to also help with survival. So, this may in fact help us to think about whether or not we should use Denosumab to both maintain bone health and as a form of adjuvant therapy in this very select patient population that is postmenopausal women with receptor positive breast cancer, who are receiving aromatase inhibitors. And some these trials really support the notion that we must have longterm follow up for hormone receptor positive breast cancer patients when we're looking at these endocrine therapies and I applaud all four trialists for bringing us to the conclusion.
Related Videos
The ASCO Post Staff
Carryn M. Anderson, MD, of the University of Iowa Hospital, discusses phase III results of the ROMAN trial of avasopasem manganese for patients with severe oral mucositis who are receiving chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced, nonmetastatic head and neck cancer. Compared with placebo, avasopasem manganese improved severe oral mucositis (Abstract 6005).
The ASCO Post Staff
Stephanie Walker, a former nurse and current activist with the Metastatic Breast Cancer Alliance, discusses findings from the BECOME project (Black Experience of Clinical Trials and Opportunities for Meaningful Engagement). They show that, even though Black patients comprise between 4% and 6% of all clinical trial participants, Black women with metastatic breast cancer are willing to consider taking part if steps were taken to increase their awareness, build trust through clear communication with health-care providers, involve people of shared racial/ethnic identity and health experience, and help patients find and access trials (Abstract 1014).
The ASCO Post Staff
Richard Finn, MD, of the Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA and the Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center, discusses analyses from the PALOMA-2 trial on overall survival with first-line palbociclib plus letrozole vs placebo plus letrozole in women with ER-positive/HER2-negative advanced breast cancer. The study met its primary endpoint of improving progression-free survival but not the secondary endpoint of overall survival. Although patients receiving palbociclib plus letrozole had numerically longer overall survival than those receiving placebo plus letrozole, the results were not statistically significant (Abstract LBA1003).
The ASCO Post Staff
Neal D. Shore, MD, of the Carolina Urologic Research Center, discusses his study findings, showing that germline genetic testing influenced care for patients with prostate cancer. Men whose genetic test was positive for a pathogenic germline variant received more recommendations for changes to follow-up and treatment, and for testing and counseling of relatives, than did patients with negative or uncertain test results (Abstract 10500).
The ASCO Post Staff
Sue S. Yom, MD, PhD, of the University of California, San Francisco, discusses a translational analysis from the NRG-HN002 study. This phase II trial established the feasibility of the tumor tissue–modified viral (TTMV) human papillomavirus DNA assay in clinical trial specimens. The goal is to use such an assay to measure tumor volume, levels of TTMV over the course of treatment, and the association of TTMV to treatment outcomes (Abstract 6006).