Courtney D. DiNardo, MD, on AML: Venetoclax and Azacitidine for Treatment-Naive Patients
EHA25 Virtual
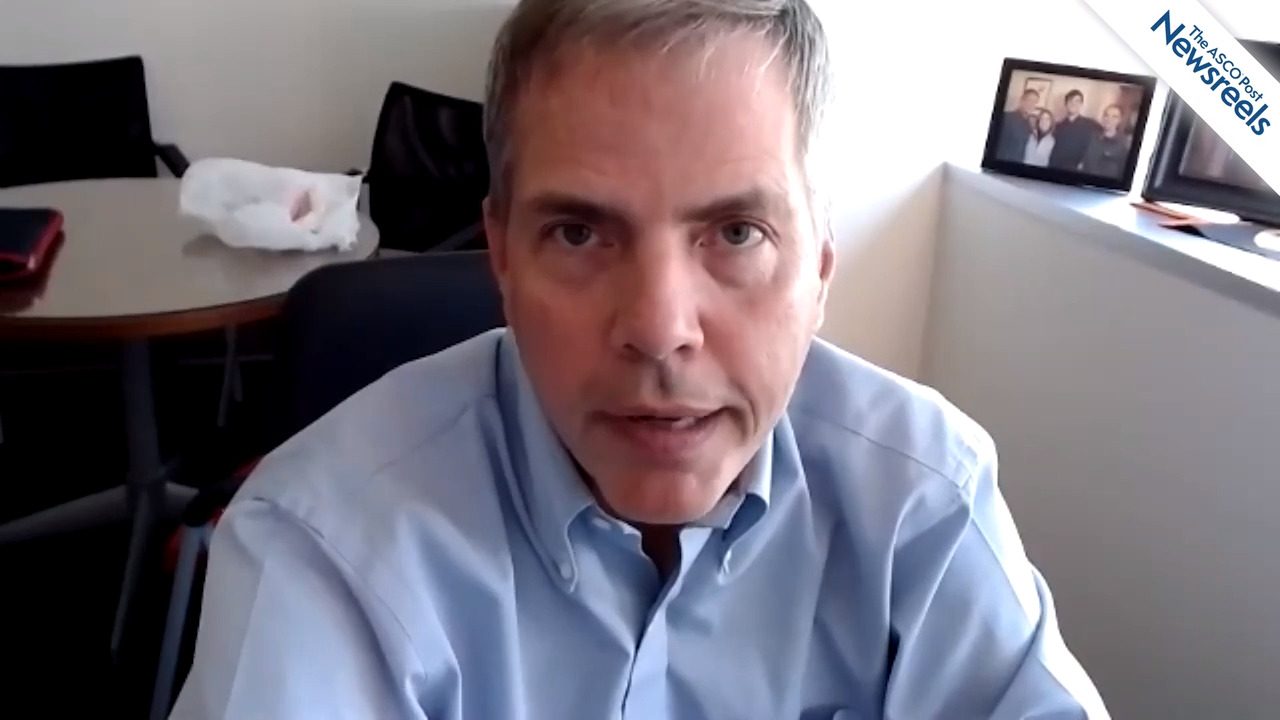
Courtney D. DiNardo, MD, of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, discusses data from her study of treatment-naive, predominantly older patients with acute myeloid leukemia who are ineligible for intensive therapy. The research shows venetoclax plus azacitidine improved response rates and overall survival compared with azacitidine alone (Abstract LB2601).
The ASCO Post Staff
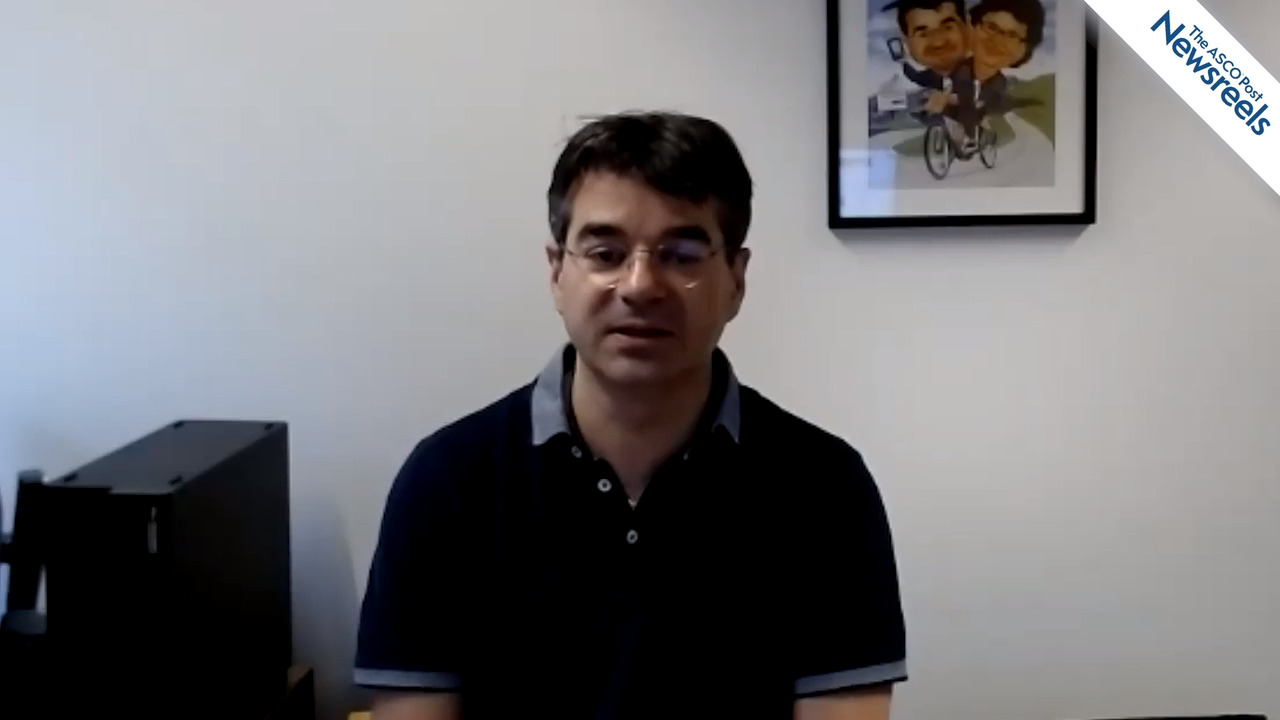
John C. Byrd, MD, of The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center, discusses the mature results of a phase II study showing durable remissions and long-term tolerability of acalabrutinib in treatment-naive patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia or small lymphocytic lymphoma (Abstract S163).
The ASCO Post Staff
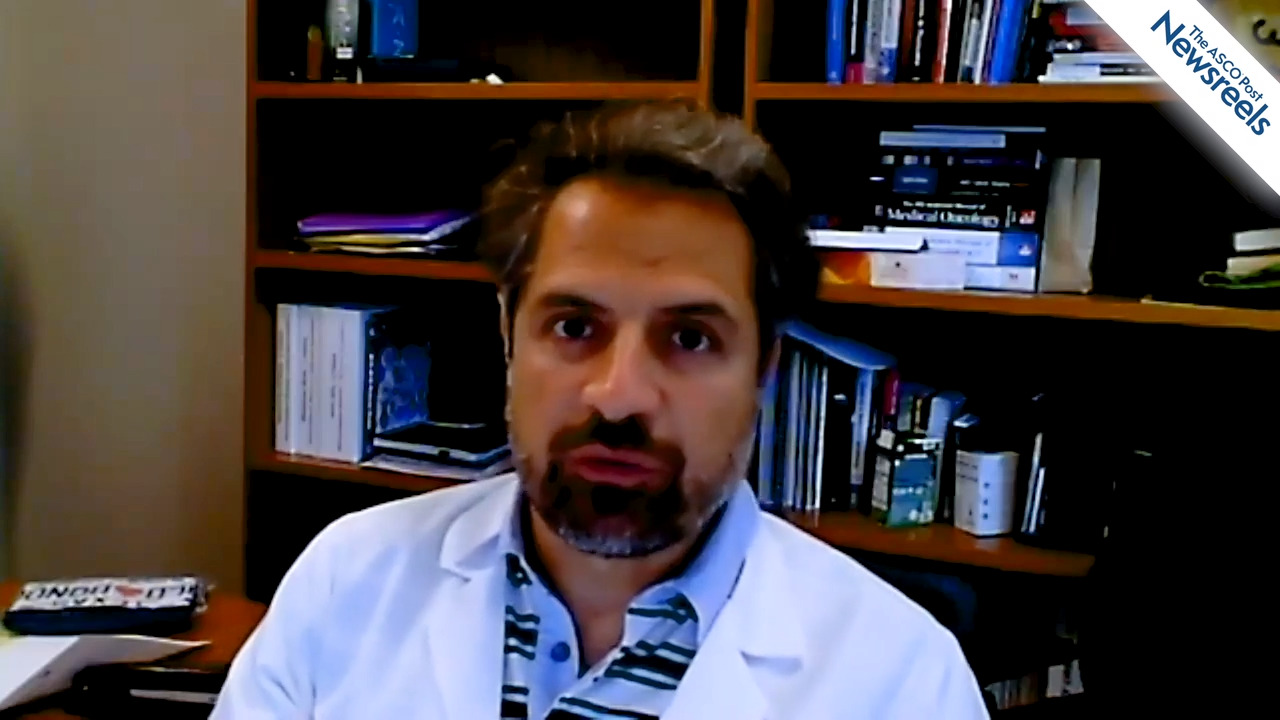
Arnon P. Kater, MD, PhD, of the University of Amsterdam, Cancer Center Amsterdam, discusses phase IIIb results from the VENICE I trial, which confirmed that venetoclax monotherapy can achieve deep responses and has a tolerable and manageable safety profile in patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (Abstract S156).
The ASCO Post Staff
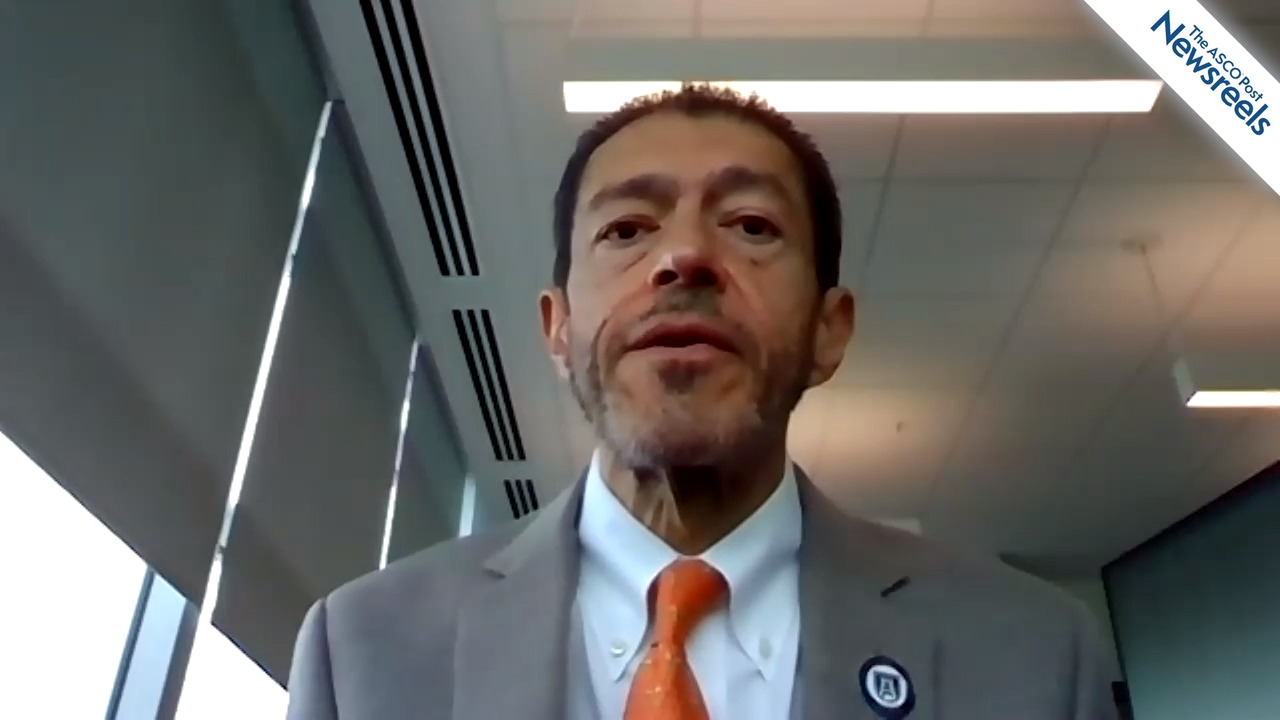
Elias Jabbour, MD, of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, discusses study findings that showed venetoclax and navitoclax with chemotherapy is well tolerated, with promising efficacy in heavily pretreated patients with relapsed or refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia and lymphoblastic lymphoma. Clinical follow-up, correlative biomarker analysis, and expansion cohort enrollment to assess discontinuous dosing are underway (Abstract S116).
The ASCO Post Staff
Anthony Moorman, PhD, of Newcastle University, discusses preliminary data showing high-risk patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia and ABL-class mutations may have improved outcomes when a tyrosine kinase inhibitor is added to chemotherapy (Abstract S117).
The ASCO Post Staff
Jorge E. Cortes, MD, of Georgia Cancer Center, discusses interim results from the OPTIC study, which showed a trend toward dose-dependent efficacy and safety, and may provide a refined understanding of the ponatinib benefit/risk profile and its relation to dose. Mature data from continued follow-up may support an alternate dosing regimen for patients with chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia (Abstract S172).