Giorgio V. Scagliotti, MD, PhD, on Doubling the Lung Cancer Cure Rate by 2025: A Realistic Goal
IASLC 2020 World Conference on Lung Cancer in Singapore
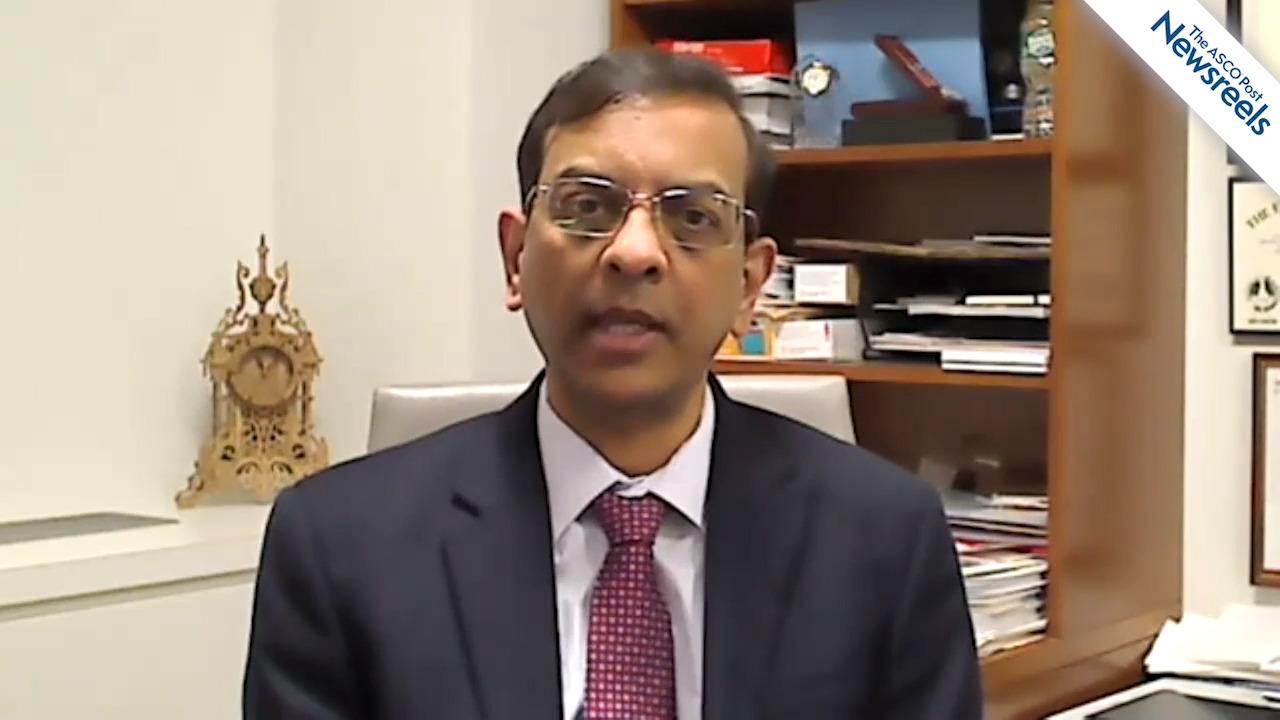
Giorgio V. Scagliotti, MD, PhD, of the University of Torino, talks about why he believes that many more patients with lung cancer can be cured within the next 4 years, given decreases in mortality rates, widespread use of targeted treatments and immunotherapies, and earlier diagnoses as a result of systematic screening with low-dose CT (Abstract PL05.08).
The ASCO Post Staff
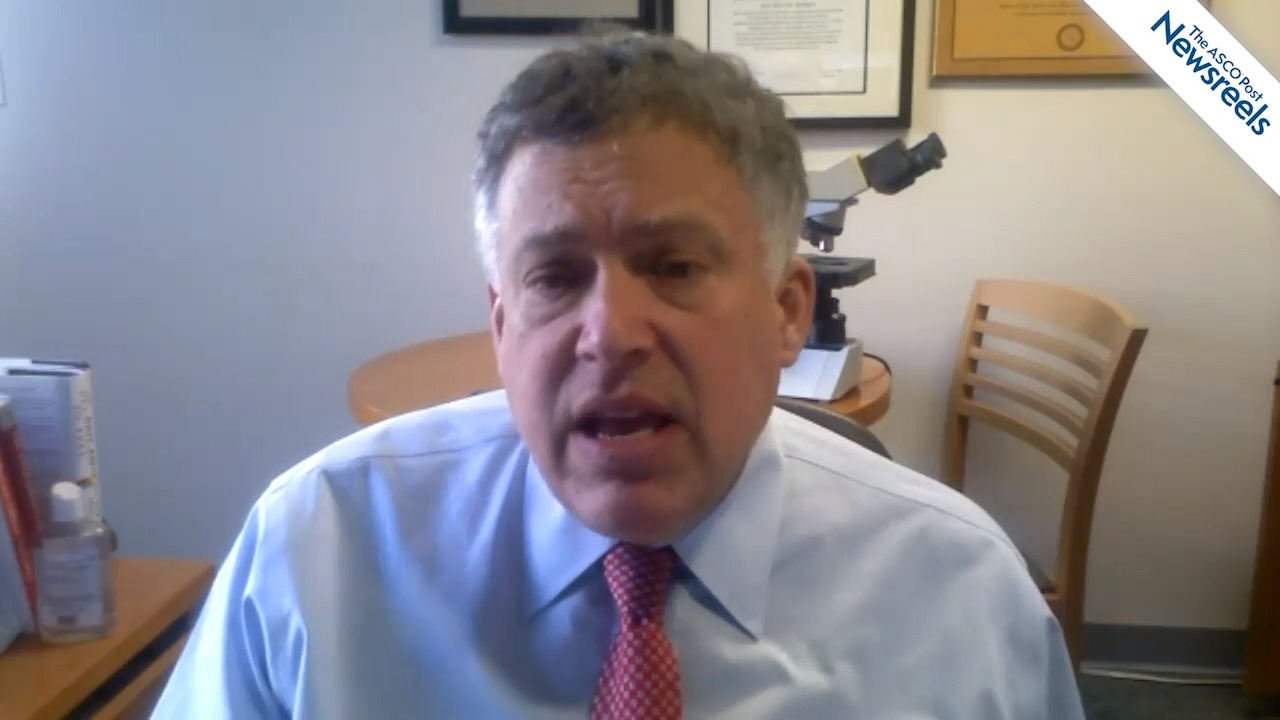
Prasad S. Adusumilli, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, discusses ongoing CAR T-cell therapy clinical trials for solid tumors, the key determinants of success for developing this treatment, and some study results to date (Abstract PL03.05).
The ASCO Post Staff
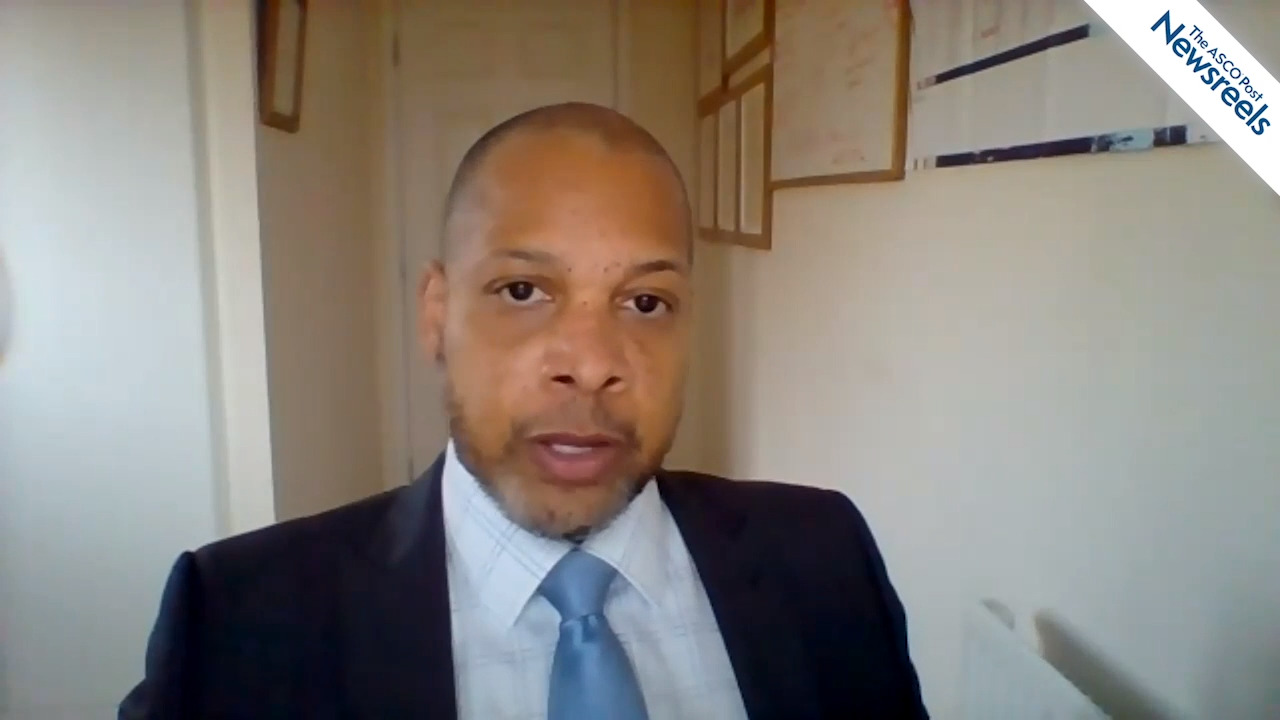
Dean Fennell, FRCP, PhD, of the University of Leicester, discusses phase III results from the CONFIRM trial, which sought a standard immunotherapy treatment to improve overall survival for patients with mesothelioma who have relapsed after taking pemetrexed and cisplatin. Globally, the incidence of mesothelioma is on the rise; in the United Kingdom alone, it has gone up nearly 500% since the 1970s (Abstract PS01.11).
The ASCO Post Staff
Roy S. Herbst, MD, PhD, of Yale University, discusses results from the LUNG-MAP Master Protocol, which support the planned use of circulating tumor DNA for enrollment onto LUNG-MAP substudies, with a positive finding meriting inclusion in study; a negative finding, while considered inconclusive, requires the use of tissue samples (Abstract MA08.10).
The ASCO Post Staff
Jill Feldman, a patient advocate who has lost five family members to lung cancer and is herself a 12-year cancer survivor living with EGFR-positive disease, describes her family history of cancer, how she has worked with her physicians for more than a decade to survive her own diagnosis, and the message she would like all oncologists to hear.
The ASCO Post Staff
Jill Feldman, a patient advocate and lung cancer survivor, discusses the current challenges and potential solutions to including more people of color and those in underserved communities in clinical trial research (Abstract PL04.06).