The first study to use x-rays and computed tomography (CT) to detect evidence of cancer among the skeletal remains of a preindustrial population suggests that between 9% to 14% of adults in medieval Britain had the disease at the time of their death. These findings were published by Mitchell et al in the journal Cancer.
This puts cancer prevalence in a time before exposure to tumor-inducing chemicals from industry and tobacco at around ten times higher than previously thought, according to the study’s researchers.
Current Study Findings
Prior research into historic cancer rates using the archaeologic record has been limited to examining the bone exterior for lesions. The previous findings suggested that cancer was rare, affecting less than 1% of the population. A team led by researchers at the University of Cambridge have now coupled visual inspection with radiologic imaging to analyze 143 skeletons from six medieval cemeteries in and around the city of Cambridge, United Kingdom, dating from the 6th to the 16th century.
“The majority of cancers form in soft-tissue organs long since degraded in medieval remains. Only some cancer spreads to bone, and of these, only a few are visible on its surface, so we searched within the bone for signs of malignancy," said lead author Piers D. Mitchell, MD, who conducted the research as part of the After the Plague project.
"Modern research shows a third to a half of people with soft-tissue cancers will find the tumor spreads to their bones. We combined this data with evidence of bone metastasis from our study to estimate cancer rates for medieval Britain. We think the total proportion of the medieval population that probably suffered with a cancer somewhere in their body was between 9% and 14%," said Dr. Mitchell, of Cambridge University's Department of Archaeology.

Excavated medieval bone from the spine showing cancer metastases (white arrow). Credit: Jenna Dittmar.
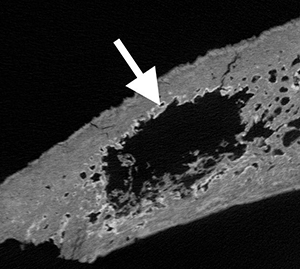
CT scan of bone from a medieval skull showing metastasis hidden within (white arrow). Credit: Bram Mulder.
"Using CT scans, we were able to see cancer lesions hidden inside a bone that looked completely normal on the outside," added study co-author and After the Plague researcher Jenna M. Dittmar, PhD.
"Until now, it was thought that the most significant causes of ill health in medieval people were infectious diseases, such as dysentery and bubonic plague, along with malnutrition and injuries due to accidents or warfare. We now have to add cancer as one of the major classes of disease that afflicted medieval people," said Dr. Dittmar.
However, the researchers pointed out that in modern Britain, some 40% to 50% of people have cancer by the time they die, making the disease three to four times more common today than the latest study suggests it was during medieval times.
They say that a variety of factors likely contribute to contemporary rates of the disease, such as the effects of tobacco, which began to be imported into Britain in the 16th century with the colonizing of the Americas. The researchers also pointed to the cancerous effects of pollutants that have become ubiquitous since the industrial revolution of the 18th century, as well as the possibility that DNA-damaging viruses are now more widespread with long-distance travel. Moreover, our longer lifespans give cancer much more time to develop.
Imaging the Remains
The skeletal remains investigated for the latest study came from sites near three villages in the vicinity of Cambridge, as well as three cemeteries uncovered within the medieval center of the university city, including the site of a former Augustinian friar and the site of a former charitable hospital that cared for the sick and destitute (now part of St. John's College).
Very few of the excavated remains were complete, so the team limited themselves to individuals with intact spinal column, pelvis, and femora. Modern research shows these to be the bones most likely to contain metastases in people with cancer.
The remains of 96 men, 46 women, and an individual of unknown sex had their vertebrae, femurs, and pelvis inspected and then imaged using x-rays and CT scans. The team found signs of malignancy in the bones of five individuals—a minimum prevalence of 3.5%. These were mostly in the pelvis, although one middle-aged man had small lesions throughout his skeleton, suggesting a form of blood cancer.
Research shows that CT scans detect bone metastases around 75% of the time, and only a third to half of cancer deaths involve spread to the bone, so the team projected that 9% to 14% of medieval Britons developed cancer.
However, they cautioned that the sample size is inevitably limited, and that diagnosing cancer in those lain dead for many centuries is somewhat challenging.
"We need further studies using CT scanning of apparently normal skeletons in different regions and time periods to see how common cancer was in key civilizations of the past," added Dr. Mitchell.
Disclosure: For full disclosures of the study authors, visit acsjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com.

