In the Clinic provides overviews of novel oncology agents, addressing indications, mechanisms, administration recommendations, safety profiles, and other essential information needed for the appropriate clinical use of these drugs.
Indication
 In January 2012, imatinib mesylate (Gleevec) was granted regular approval for use in adult patients as adjuvant treatment following complete gross resection of Kit (CD117)-positive gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST).1 Imatinib had received accelerated approval in this indication in 2008. Labeling for this indication has been updated with results of a phase III trial showing that recurrence-free and overall survival were improved by continuing adjuvant imatinib therapy to 36 months compared with 12 months.
In January 2012, imatinib mesylate (Gleevec) was granted regular approval for use in adult patients as adjuvant treatment following complete gross resection of Kit (CD117)-positive gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST).1 Imatinib had received accelerated approval in this indication in 2008. Labeling for this indication has been updated with results of a phase III trial showing that recurrence-free and overall survival were improved by continuing adjuvant imatinib therapy to 36 months compared with 12 months.
Imatinib has prior indications in Philadelphia chromosome–positive chronic myeloid leukemia, myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative diseases, aggressive systemic mastocytosis, hypereosinophilic syndrome/chronic eosinophilic leukemia, dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, and Kit-positive unresectable/metastatic malignant GIST.
 In a phase III open-label trial,2 397 patients undergoing surgical resection of Kit-positive GIST were randomized to receive 12 (n = 199) or 36 (n = 198) months of imatinib at 400 mg/d. Patients had to have a tumor diameter > 5 cm and mitotic count > 5/50 high-power fields, tumor diameter > 10 cm and any mitotic count, or tumor of any size with mitotic count > 10/50 high-powerfields, or a tumor ruptured into the peritoneal cavity. Patients had a median age of 61 years.
In a phase III open-label trial,2 397 patients undergoing surgical resection of Kit-positive GIST were randomized to receive 12 (n = 199) or 36 (n = 198) months of imatinib at 400 mg/d. Patients had to have a tumor diameter > 5 cm and mitotic count > 5/50 high-power fields, tumor diameter > 10 cm and any mitotic count, or tumor of any size with mitotic count > 10/50 high-powerfields, or a tumor ruptured into the peritoneal cavity. Patients had a median age of 61 years.
Median follow up durations were 42 months for patients without a relapse event and 48 months for patients still living. Relapse events occurred in 42% of patients in the 12-month arm and 25% of patients in the 36-month arm, representing a significant 54% reduction in risk of relapse with 36-month treatment (HR = 0.46, P < .0001). Death occurred in 13% of patients in the 12-month arm vs 6% of patients in the 36-month arm, representing a significant 55% reduction in risk for death with 36-month treatment (HR = 0.45, P = .0187).
How It Works
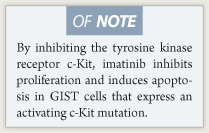
 Imatinib inhibits receptor tyrosine kinases for bcr-abl, platelet-derived growth factor, and stem cell factor (c-Kit). Thus, imatinib inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in GIST cells that express an activating c-Kit mutation.
Imatinib inhibits receptor tyrosine kinases for bcr-abl, platelet-derived growth factor, and stem cell factor (c-Kit). Thus, imatinib inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in GIST cells that express an activating c-Kit mutation.
How It Is Given
As adjuvant treatment following complete gross resection of GIST, imatinib is dosed at 400 mg once daily, with treatment for 3 years recommended. The optimal duration of imatinib treatment in this setting is not known.
Imatinib should be taken with food and a large glass of water to avoid gastrointestinal irritation. Imatinib is metabolized by the CYP3A4 isoenzyme. Since significant reductions in imatinib concentration may occur when imatinib is administered concomitantly with strong CYP3A4 inducers (for example, many anticonvulsants, barbiturates, and St. John's Wort), such agents should be avoided. If concomitant use of a strong CYP3A4 inducer is necessary, the dosage of imatinib should be increased by at least 50% and clinical response should be carefully monitored. Dosage adjustments are required in patients with moderate renal impairment.
Safety Profile
 In the trial described above, the most common adverse events were similar to those observed in other imatinib trials and included edema, nausea, vomiting, muscle cramps, bone or muscle pain, diarrhea, rash, fatigue, and abdominal pain. Discontinuation of imatinib therapy due to adverse events occurred in 8% and 14% of patients in the 12- and 36-month arms, respectively. In a prior adjuvant GIST trial, treatment was discontinued for adverse events in 17% of imatinib patients and 3% of placebo patients, with edema, gastrointestinal disturbances (nausea, vomiting, abdominal distention, and diarrhea), fatigue, low hemoglobin, and rash being the most frequently reported adverse events at the time of discontinuation.
In the trial described above, the most common adverse events were similar to those observed in other imatinib trials and included edema, nausea, vomiting, muscle cramps, bone or muscle pain, diarrhea, rash, fatigue, and abdominal pain. Discontinuation of imatinib therapy due to adverse events occurred in 8% and 14% of patients in the 12- and 36-month arms, respectively. In a prior adjuvant GIST trial, treatment was discontinued for adverse events in 17% of imatinib patients and 3% of placebo patients, with edema, gastrointestinal disturbances (nausea, vomiting, abdominal distention, and diarrhea), fatigue, low hemoglobin, and rash being the most frequently reported adverse events at the time of discontinuation.
In adjuvant trials, adverse events of grade 3 or higher observed in imatinib recipients included increased alanine aminotransferase (3% vs 0% for placebo), increased aspartate aminotransferase (2% vs 0%), decreased neutrophil count (3% vs 1%), and decreased hemoglobin (1% vs 0%) among laboratory abnormalities. Clinical adverse events included abdominal pain (3% vs 1%), diarrhea (3% vs 1%), rash (3% vs 0%), fatigue (2% vs 1%), nausea (2% vs 1%), vomiting (2% vs 1%), and periorbital edema (1% vs 0%). ■
References
1. U.S. Food and Drug Administration: Imatinib mesylate tablets. Available at www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm289789.htm. Accessed March 23, 2012.
2. GLEEVEC (imatinib mesylate) tablets prescribing information. Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation, January 2012. Available at www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/021588s035lbl.pdf. Accessed March 23, 2012.

