In the phase III IsKia trial in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma, therapy incorporating the CD38-directed monoclonal antibody isatuximab-irfc with a carfilzomib-based regimen led to high rates of minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity at postconsolidation cutoffs, as reported at the 2023 American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting and Exposition by Francesca Gay, MD, PhD, Associate Professor in the Department of Molecular Biotechnology and Health Sciences at the University of Torino in Italy, and hematologist at the Azienda Ospedaliero-Universitaria Città della Salute e della Scienza di Torino.1

“With longer follow-up, this trial can offer the opportunity to explore the correlation between depth of MRD negativity and progression-free and overall survival….”— FRANCESCA GAY, MD, PhD
Tweet this quote
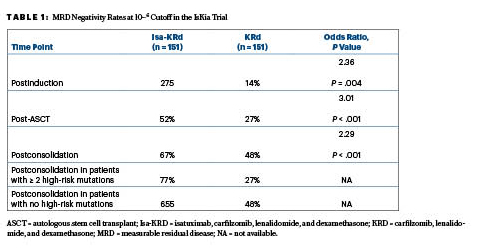
Following consolidation, the quadruplet of isatuximab, carfilzomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (Isa-KRd) significantly increased the rates of MRD negativity at the 10−5 and 10-6 cutoffs, as compared to the KRd triplet. The primary endpoint, MRD negativity by next-generation sequencing at a 10−5 cutoff after consolidation,indicated a significant advantage for Isa-KRd over KRd, based on rates of 77% vs 67%.This advantage was also seen at the more stringent 10−6 cutoff, with rates of 67% and 48%, respectively, Dr. Gay reported at the ASH Plenary Session.
“The primary endpoint of the study was met. The rate of MRD negativity by intention-to-treat analysis was significantly higher with Isa-KRd vs KRd,” Dr. Gay said. “With longer follow-up, this trial can offer the opportunity to explore the correlation between depth of MRD negativity and progression-free and overall survival…. MRD negativity is potentially a good surrogate endpoint.
IsKia Design
The study enrolled 302 patients < 70 years of age with newly diagnosed stage I to IV multiple myeloma. About half the patients were considered at standard risk, and the other half had one or more unfavorable cytogenetic risk factors.
KEY POINTS
- Progression-free survival and overall survival are increasingly becoming difficult endpoints to achieve in clinical trials, thanks to the efficacy of newer treatments in multiple myeloma.
- The phase III IsKia trial evaluated the addition of daratumumab to carfilzomib, lenalidomide and dexamethasone (Isa-KRd) vs KRd alone, using minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity as the primary endpoint.
- Following consolidation, Isa-KRd significantly increased MRD negativity at the 10−5 and 10−6 cutoffs as compared to the KRd triplet: 77% vs 67% at the 10−5 cutoff.
Patients in the KRd arm received four 28-day induction cycles of carfilzomib at 20 mg/m2 on day 1 of cycle 1 followed by 56 mg/m2 on days 8 and 15 of cycle 1 and on days 1, 8, and 15 for cycles 2 to 4, plus lenalidomide at 25 mg/d and dexamethasone at 40 mg at standard dosing. Those in the Isa-KRd arm received the same KRd regimen plus isatuximab at 10 mg/kg on days 1, 8, 15, and 22 during cycle 1 followed by 10 mg/kg on days 1 and 15 during cycles 2 to 4. Patients underwent stem cell collection, high-dose chemotherapy, and autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT), followed by consolidation therapy.
Striking Improvement in MRD Negativity
At a median follow-up of 21 months, striking differences were seen between the regimens at the MRD 10−5 cutoff (the primary endpoint) and at the 10−6 cutoff, with MRD negativity rates increasing over time. “The increase in MRD negativity rate in the Isa-KRd arm was seen in all the subgroups of patients analyzed at the 10−5 and 10−6 cutoffs. Interestingly, this was true for standard-risk, high-risk, and very high–risk patients,” Dr. Gay noted. At least 97% of the MRD samples were evaluable at these two thresholds, she noted.
After ASCT, at 10−5 the MRD negativity rates were 64% with Isa-KRd vs 49% with KRd (odds ratio [OR] = 1.93; P = .006); the postconsolidation MRD rates were 77% and 67%, respectively (OR = 1.67; P = .049). Following consolidation, 94% of each arm achieved at least a very good partial response, while 74% and 72%, respectively, had a complete response.
“In the context of this highly effective regimen that produced a high rate of response, the 10−6 MRD negativity cutoff might be a more informative response category,” she said. These response rates, including those in favorable vs very unfavorable cytogenetic risk groups, are shown in Table 1.
Treatment-related adverse events of any grade were observed in 55% of the Isa-KRd arm vs 44% of the KRd arm, most commonly neutropenia (41% vs 26%), thrombocytopenia (34% vs 25%), and anemia (21% vs 19%), respectively. Grade 3 to 4 toxicities were reported for 40% and 30% of patients, respectively. Nonhematologic toxicities of any grade included SARS-CoV-2 infection (26% vs 19%), other infections (36% vs 32%), cardiac disorders (7% vs 13%), and thromboembolisms (8% vs 11%).
DISCLOSURE: Dr. Gay has received honoraria from AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene, Sanofi, GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer, Takeda, Janssen, and Amgen; and has served on advisory boards for AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene, Sanofi, Roche, GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer, Oncopeptides, Takeda, Janssen, and Amgen.
REFERENCE
1. Gay F, Roeloffzen W, Dimopoulos MA, et al: Results of the phase III randomized IsKia trial: Isatuximab-carfilzomib-lenalidomide-dexamethasone vs carfilzomib-lenalidomide-dexamethasone as pre-transplant induction and post-transplant consolidation in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients. 2023 ASH Annual Meeting & Exposition. Abstract 4. Presented December 10, 2023.


