Paula Aristizabal, MD, MAS, on Surviving Childhood Leukemia Near the Border of the United States and Mexico
2023 ASCO Annual Meeting
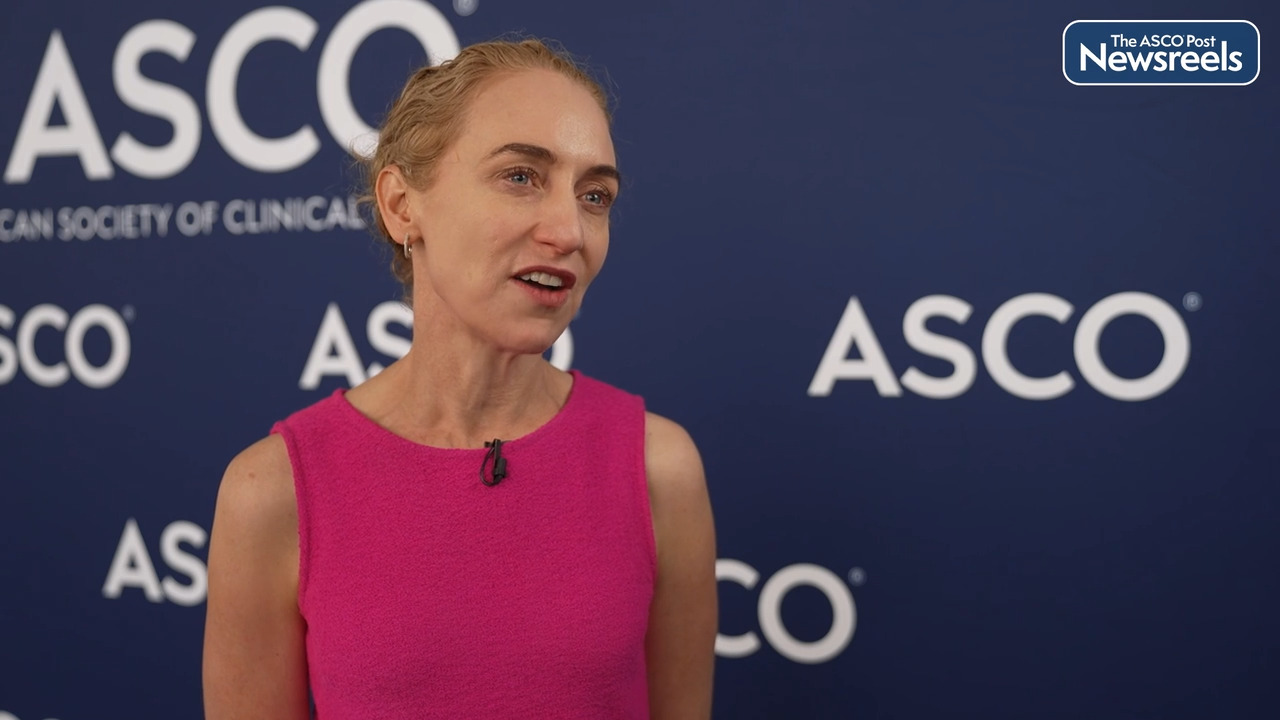
Paula Aristizabal, MD, MAS, of the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, talks about using a health systems strengthening approach to improve leukemia care and survival in a public Mexican hospital in the region of the border between the United States and Mexico. The demonstrated increase in overall survival across a decade after implementation of the program seems to validate the use of such models, not only to improve clinical outcomes, but also to build sustainable hospital capacity, financially and organizationally (Abstract 1502).
Transcript
Disclaimer: This video transcript has not been proofread or edited and may contain errors.
Paula Aristizabal, MD:
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia is the most common childhood cancer and survival has improved dramatically in high income countries to rates over 80%. Unfortunately, in low and middle income countries, survival has not increased at the same pace. For example, in Mexico, a low income country that is just across the border from the US, survival range is between 10% and 60%. Since in San Diego we share a border with Tijuana, we saw the disparities and we thought that it was our social responsibility to do something about it so we implemented a twinning program and twinning involves when a center of excellence in a high income country partners and collaborates with a center in a low, middle income country. We started this twinning program in 2008 in collaboration with St. Jude Children's Research Hospital, and we were able to implement a new team in Tijuana that was able to provide the best care possible for all the pediatric cancers.
Then in 2013, we realized that the burden of leukemia was getting higher and higher and we decided to implement a new model of health system strengthening called the WHO Framework for Action. The WHO Framework for Action has six building blocks that provide all the elements to improve care in a health system. We incorporated the WHO Framework for Action into the already existing twinning model to improve leukemia survival. We provided training to the team in Tijuana. We provided protocols that they could adapt. We provided mentorship and we provided support for a new infrastructure to develop the best possible leukemia care for children with with leukemia in Baja, California, Mexico.
After the implementation of the program, survival for leukemia improved from 59% to 65% and, importantly, the survival for standard risk leukemia improved from 73% before implementing the program to 100%, which is totally amazing because that is the same survival that we have in San Diego, just 20 miles from Tijuana. Survival for high risk leukemia improved from 48% to 55%. It wasn't so significant but we know that that is an area of improvement that we hope that we can tackle in our next steps of the program. Our model in Tijuana, combining a twinning program with the WHO Framework for Action, was effective in improving survival in a low and middle income country. This model can be applicable to a partnership between a high income country and a low, middle income country, especially in regions that share a border but also in other low and middle income countries remotely. Something that we learned from COVID is that you can apply many of these models working remotely and we are extremely pleased with these results. Our next steps include the improvement of the survival for patients with high risk leukemia.
Ajay K. Nooka, MBBS, of Winship Cancer Center of Emory University, discusses findings from a pooled analysis of MagnetisMM studies. The data showed that, in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma who have not yet been treated with B-cell maturation antigen–directed therapies, elranatamab was efficacious and well tolerated.
The ASCO Post Staff
Lisa M. DeAngelis, MD, and Ingo K. Mellinghoff, MD, both of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, discuss findings from the INDIGO trial showing that the IDH1/2 inhibitor vorasidenib improves progression-free survival for patients with residual or recurrent grade 2 glioma with an IDH1/2 mutation. These data demonstrate the clinical benefit of vorasidenib in this patient population for whom chemotherapy and radiotherapy are being delayed.
The ASCO Post Staff
Georgina V. Long, MD, PhD, of Melanoma Institute Australia and The University of Sydney, discusses new data showing that patients with resected stage IIB/C melanoma who were treated with adjuvant nivolumab had prolonged recurrence-free survival compared with placebo across all biomarker subgroups. The baseline biomarkers most predictive of prolonged recurrence-free survival with nivolumab were high interferon gamma score, high tumor mutational burden, CD8 T-cell infiltration, and low C-reactive protein (Abstract 9504).
The ASCO Post Staff
Narjust Florez, MD, of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, and Ticiana Leal, MD, of Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University, discuss the use of tumor treating fields therapy, in which electric fields disrupt processes critical for cancer cell viability. Already approved by the FDA to treat glioblastoma and mesothelioma, the treatment has extended overall survival in this phase III study of patients with metastatic non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with progression on or after platinum-based chemotherapy, without exacerbating systemic toxicities (Abstract LBA9005).
The ASCO Post Staff
Jennifer A. Ligibel, MD, of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, discusses a telephone-based weight loss intervention that induced clinically meaningful weight loss in patients with breast cancer who had overweight and obesity, across demographic and tumor factors. Additional tailoring of the intervention may possibly enhance weight loss in Black and younger patients as well (Abstract 12001).